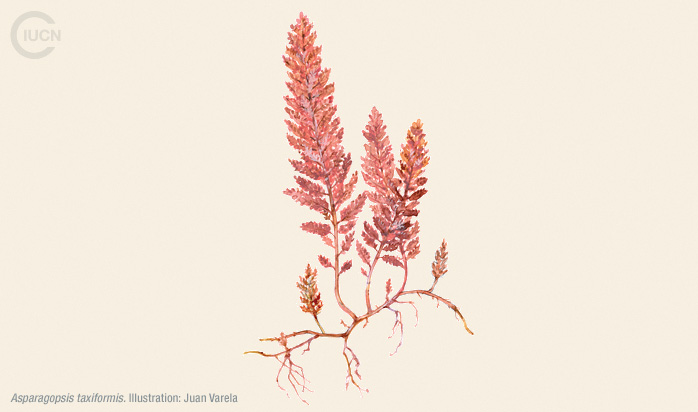
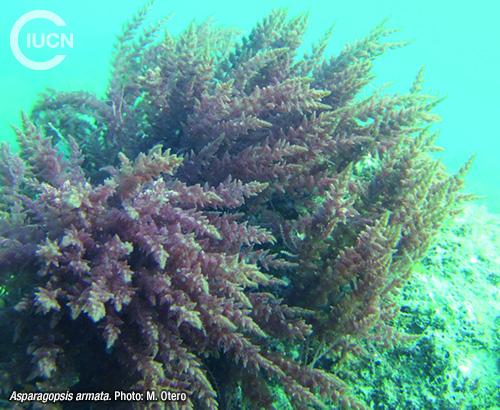
Asparagopsis taxiformis
Information
This species usually grows on infralittoral rocky bottoms from the sea surface to a depth of 50 m. The sporophyte stage (Falkenbergia hillebrandii) is filamentous, rose-red in colour, much branched and forming dense cotton-wool-like tufts 15 mm in diameter. Asparagopsis taxiformis can be an epiphyte on other organisms, especially on Corallina species, colonizing many different habitats from littoral pools to rocky bottoms down to 20 m in depth.
It is able to reproduce sexually and asexually and has a macroscopic gametophyte phase, referred to as Asparagopsis, and a macroscopic tetrasporophyte phase known as the ‘Falkenbergia’ stage.
Its highly successful vegetative reproduction may account for the rapid spread of the species, which has an attachment system consisting of basal stolons and rhizoids that facilitate the establishment of reproductive fragments.
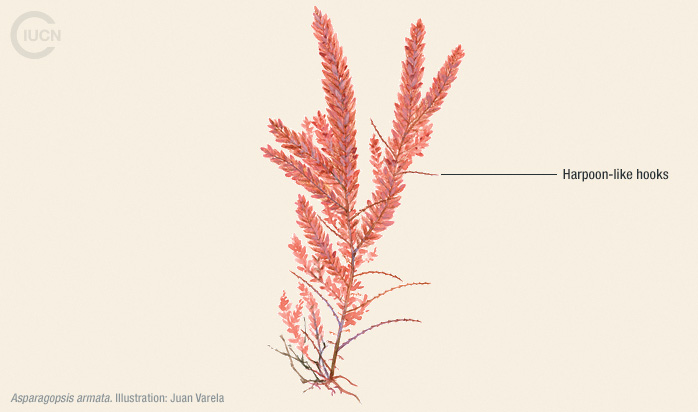
This species resembles Asparagopsis armata; however, the presence of harpoon-like hooks in the gametophyte stage of A. armata and the absence of them in A. taxiformis is a distinguishing character. The tetrasporophyte of A. taxiformis is, however, apparently indistinguishable from that of A. armata.
The genus as a whole is noted for its high invasive potential.


Native to Western Australia, this species shows invasive behaviour around the Indo-Pacific region, including Japan and Hawaii. Asparagopsis taxiformis was probably introduced to the Mediterranean via maritime transport, and is currently widespread throughout the Mediterranean and along the Atlantic coast of Europe.
Unknown, but it probably outcompetes native species for space and light.
Unknown. Trials have shown the potential pharmaceutical compounds of antifungal and antibiotic activity of this algae.
Altamirano J. et al. 2008. The invasive species Asparagopsis taxiformis (Bonnemaisoniales, Rhodophyta) on Andalusian coasts (Southern Spain): reproductive stages, new records and invaded comunities. Acta Botánica Malacitana, 33, 5-10.
Andreakis, N. et al., 2004. Asparagopsis taxiformis and Asparagopsis armata (Bonnemaisoniales, Rhodophyta): genetic and morphological identification of Mediterranean populations. Eur. J. Phycol. , 39: 273 – 283.